Understanding graphs
The heart of Apollo GraphOS
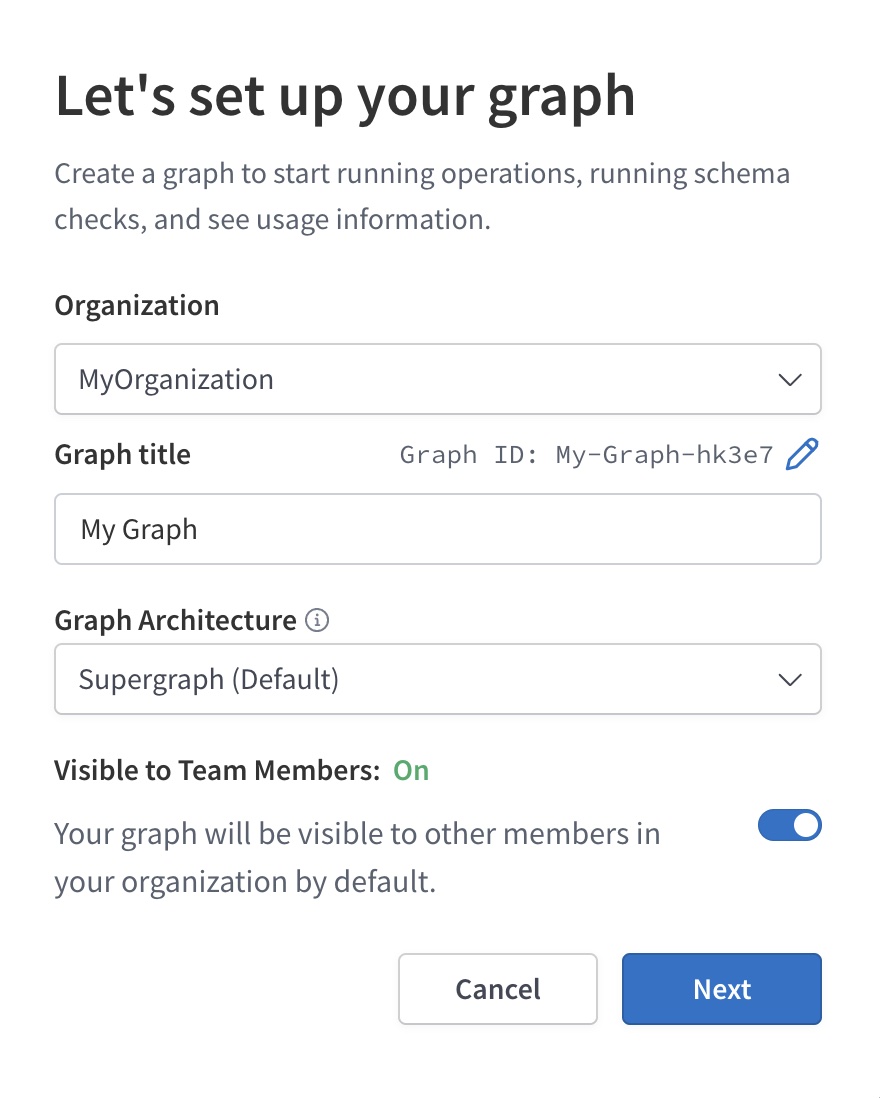
As its name suggests, GraphOS is a platform for building and managing graphs. Each graph corresponds to a GraphQL service in your organization.
A GraphQL service usually runs in more than one environment (such as staging or production), so every graph in GraphOS has one or more variants that each correspond to one environment:
Each variant of a graph keeps track of its own separate GraphQL schemas and operation metrics.
Graph types
Every graph in GraphOS is one of these graph types:
| Graph type | Description |
|---|---|
A supergraph consisting of:
Recommended for all organizations getting started with GraphOS. | |
Self-hosted supergraph (enterprise only) | A supergraph consisting of:
Recommended for enterprise organizations that require full customization of their router, usually for advanced performance or data compliance reasons. |
Not recommended. A single GraphQL service hosted in your infrastructure with no router. |
Cloud supergraphs
Cloud supergraphs require an Apollo organization on the Serverless (Free) or Serverless plan. Learn more about plans.
Cloud supergraphs are recommended for every organization that's getting started with GraphOS. For every variant of a cloud supergraph, GraphOS provisions and manages a router that acts as the variant's public endpoint. Application clients communicate with this endpoint instead of communicating directly with your GraphQL server(s):
The router automatically reports certain operation metrics to GraphOS, so you don't need to configure this reporting in your GraphQL servers.
Cloud supergraphs use an architecture called Apollo Federation. With federation, you can distribute your supergraph's capabilities across multiple GraphQL services, which are known as subgraphs. The router executes client operations across multiple subgraphs as needed:
Even if your API currently uses only one GraphQL server, a cloud supergraph helps you add more subgraphs later as your organization grows.
Self-hosted supergraphs
⚠️ Self-hosted supergraphs are a feature of Enterprise plans. If you need to host your supergraph's router in your own infrastructure, please contact us.
With a self-hosted supergraph, GraphOS does not provision a router for your supergraph. Instead, you host your supergraph's router in your own infrastructure:
Your self-hosted router is an instance of the Apollo Router (cloud supergraphs use the Apollo Router under the hood).
Self-hosted supergraphs provide full control over your router, but they also require handling its deployment and management. Before you adopt this graph type, make sure you have the necessary team structure to properly manage an additional service in your infrastructure.
Monographs
A monograph is a graph that consists of a single GraphQL server with no router:
⚠️ We strongly recommend against monographs! A monograph introduces significant technical and logistical scaling issues as more teams contribute to your graph and its schema.
Additionally, the router provides essential GraphOS functionality beyond support for multiple subgraphs: it also enables powerful features like @defer support and straightforward metrics reporting.
Creating graphs
To create a cloud supergraph, see the GraphOS quickstart.
To create a non-cloud graph (i.e., a self-hosted supergraph or a monograph), see the instructions for your organization's plan type:
Variants
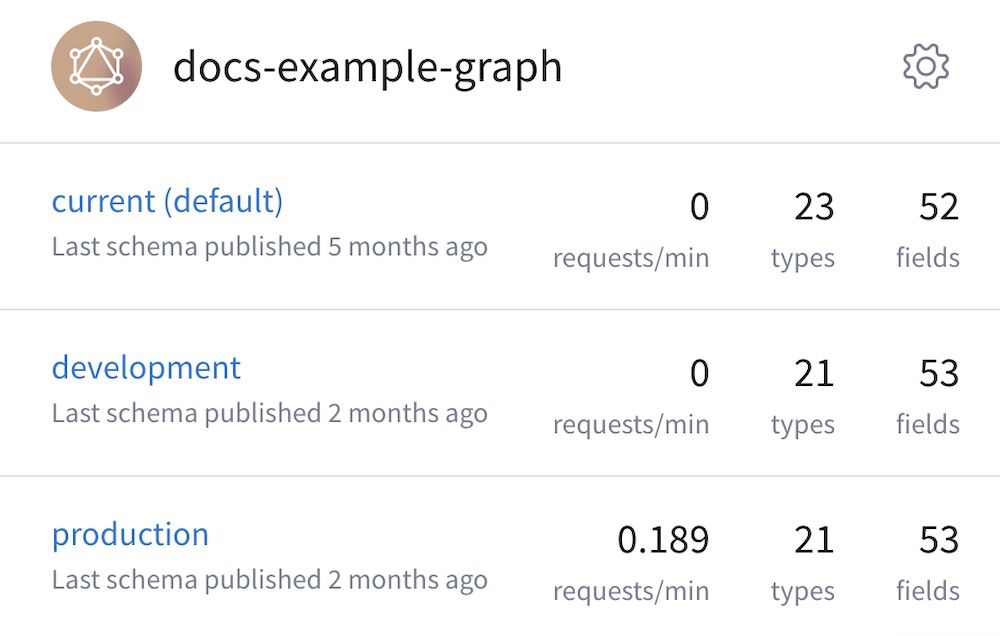
To distinguish between instances of the same graph running in different environments (such as staging and production), you define multiple variants of your graph. Each variant has its own schemas, along with its own change history and metrics.
Each of your graph's variants is shown in Apollo Studio:
Creating a variant
See this section.